
Egg & Embryo Freezing
1.Egg Freezing
Egg freezing is a new development technology. The first child born after the thawing of frozen eggs was born in 1986. However, because the subsequent success rate was not high, there was concern that the freezing process damaged the chromosome of the egg, resulting in fetal defects, so egg freezing did not flourish in the next 20 years. In recent years, due to advances in freezing methods and microinjection of single sperm in the egg, the medical community has become interested in the freezing of eggs again, resulting in a new boom.
A.Who is suitable for egg freezing?
- Young female cancer patients before receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Women who have had to have their ovaries removed (for example, some women with BRCI and BRCII mutations need to have their ovaries removed to prevent breast cancer).
- Husband cannot provide sperm during the course of IVF
- In some countries where frozen embryos are not allowed, frozen eggs can be used
- Couples who have ethical or ethical considerations for frozen embryos.
- Women over the age of 30 consider postponing fertility due to their careers.
- A woman with a family history of premature ovarian failure or Turner's Syndrome
B.How to freeze the egg:
Freezing eggs is a costly and invasive procedure. The human egg is the largest single cell in the human body. It contains a lot of water, and its outer layer is excellent in permeability. When frozen, the water in the egg will form ice crystals, and the DNA and membrane structure of the egg will be disrupted. Therefore, the use of cryoprotectants instead of water is necessary to reduce ice crystal formation. Eggs must be frozen within 2 hours after egg retrieval.
C.There are currently two egg freezing technologies:
- Slow Controlled Freeze
- Ultra-fast freezing (vitrification): After thawing, the egg has a higher survival rate and higher live birth rate.
D.Is egg freezing safe?
Egg freezing is a new technology and therefore does involve some unknown risks. However, according to current results, frozen eggs should be regarded as safe, because up to now, there have been no abnormal reports on children born from frozen eggs.
E.How successful is egg freezing?
According to literature, the survival rate of eggs after thawing is 80-90%, and the fertilization rate is 92%. The live birth rate of pregnancy is greatly different depending on the age and number of eggs frozen.
F.Embryo Freezing Process
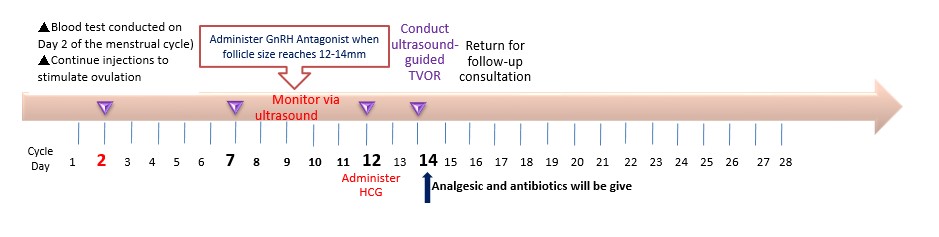
2.Embryo Freezing
After embryo transfer is done and there are surplus embryos of good quality, these can be cryopreserved and thawed in the future for another embryo transfer, providing more opportunities for pregnancy. Some patients may have overstimulated ovaries with associated discomforts which may be heightened after implantation, and may have to delay embryo transfer. Patients can have their good quality embryos cryopreserved for future thawing and embryo transfer. At present, according to the provisions of the Artificial Reproduction Law, embryos can be cryopreserved for 10 years.
3.Sperm Freezing
If there are conflicts in schedule that the husband cannot collaborate with his wife's treatment schedule, sperm can be cryopreserved ahead of time. Fresh sperm is best for couples if semen analysis reveals the sperm conditions to be suboptimal.