
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) refers to the retrieval of mature eggs from the ovaries under the guidance of ultrasound, followed by fertilization with pre-treated spermatozoa in petri dishes until the formation of embryos. These are to be cultured in vitro for several days, and then depending on personal circumstances, the embryos can be transferred into the uterus or cryo-preserved until the appropriate time for embryo thawing and implantation in the uterus.
Procedure: Blood tests are done on day 2 of the menstrual cycle to aid in the choice of the most suitable medications to stimulate ovulation. While on medication, ultrasound and blood tests are used to track follicular maturation. When follicles are mature, the patient is given human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) to trigger the final maturation of eggs. 34-36 hours later, egg retrieval is done under the guidance of vaginal ultrasound. 2 to 5 days after ova retrieval, embryo transfer is done and medications are given to assist in implantation. 7 to 9 days after the embryo transfer, blood tests are done to check for pregnancy. There are 3 different protocols to stimulate ovulation: long-acting, short-acting or antagonists. You can discuss with your dedicated physician to choose the best protocol of treatment.
Who is suitable for the IVF treatment?:
- Those with fallopian tube obstruction
- Those with severe endometriosis
- Those with severe male infertility
- Those with several failed IUI treatments
- Advanced maternal age or early aging of the ovary
-
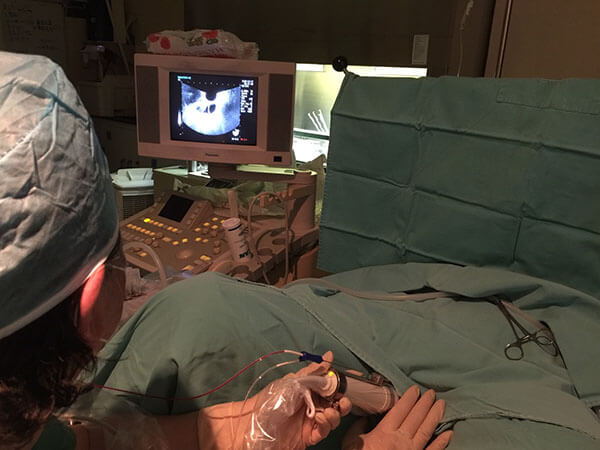
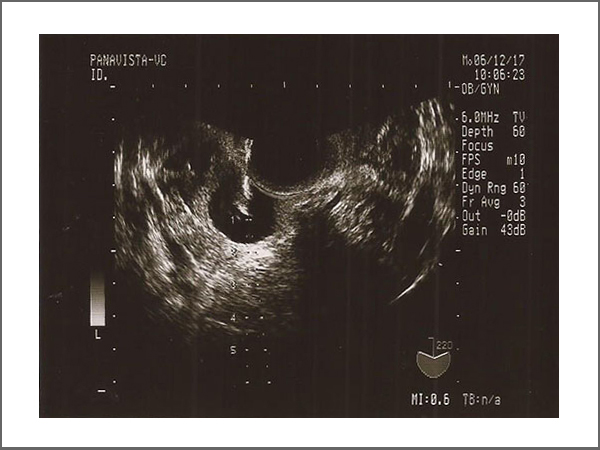
1.Ultrasound-guided Transvaginal Oocyte Retrieval (TVOR)
The entire process will be guided by ultrasound to ensure the safety and accuracy of oocyte retrieval. Depending on the number of follicles, the procedure may take 10 to 30 minutes. After being observed in the recovery room, the patient can go home. During the procedure, an intravenous anesthesia will be used and the patient will be asked to fast for 6-8 hours prior to the scheduled office procedure. There may be some pain or vaginal bleeding after the procedure. Analgesic and antibiotics will be given for relief. Patients are advised to keep in touch with us for any associated problems.
Oocyte Retrieval
Puncture Oocyte
-
2.Embryo Transfer
- Embryo transfer is done under ultrasound guidance for accuracy and precision of placement. Patients are usually requested to drink until the bladder is full before this procedure.
- Strict patient identification is confirmed before embryo transfer in the uterus. Usually the process of embryo transfer is painless and does not require the use of anesthesia.The entire process is done aseptically.
-
3.Laser Assisted Hatching
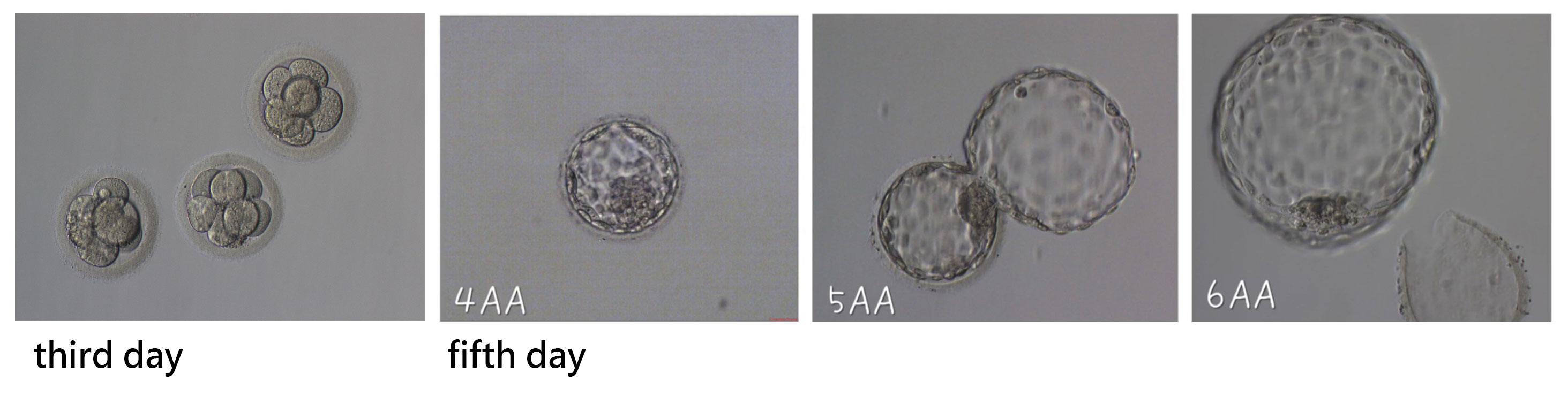
After fertilization, the embryo develops until the blastocyst performs zona hatching wherein the zona pellucida degenerates and decomposes so that implantation can occur. If the zona pellucida is too thick or too hard, it will not be conducive to the hatching of the blastocyst and uterine implantation. Our reproductive health center uses laser in the“assisted hatching”technology to make a small hole or slit in the zona pellucida to make it easier for the embryo to hatch, thus increasing the implantation rate. Precise lasers do not harm the embryos and this technique can increase the pregnancy rate for those who have many failed IVF attempts, or for those more advanced in childbearing age.
What situations can leverage laser assisted hatching:
- Those that are 38 years or older
- Those with multiple IVF failures
- Those whose transparent belt is thicker
- Those who use thawed embryos for implantation
- Those with poor embryo quality
-
4.Intra-Uterine Insemination (IUI) / Artificial Insemination (AIH)
Oral or injectable ovulation medications are started on day 3 of the menstrual cycle. Tracking of ovarian follicle size and endometrial thickness by vaginal ultrasound is started on or about day 10 of the menstrual cycle. When follicle size reaches 18 to 20mm, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is given to facilitate ovulation. Within 24-36 hours, the husband collects semen. Undergoing screening, we remove sperm with poor mobility or abnormal shapes, white blood cells, bacteria, and some chemical materials. A concentration of good and active sperm is injected into the uterine cavity through the cervix, allowing the sperm to swim to the egg and achieving fertilization in the normal course of events.
The course of treatment is approximately 2 to 3 weeks with an average pregnancy rate of 15%.
Who is suitable for the IUI treatment?
- Those with mild male infertility
- Those with presence of cervical lesions
- Those with presence of ovulatory dysfunction
- Those with presence of mild endometriosis
- Those with unexplained infertility
If success is not achieved after 2-3 treatment courses, an IVF treatment should highly be considered.